
SOAR Use Case: Hunting for Insider Threats
Insider threats refer to risks posed by individuals within an organization—whether employees, contractors, or business partners—who misuse their access to sensitive information and systems. These threats can either be malicious (intentional harm) or accidental (unintentional harm). According to CISA, insider threats can cause harm to an organization’s mission, resources, information, and infrastructure, leading to data breaches, espionage, sabotage, and significant reputational damage.
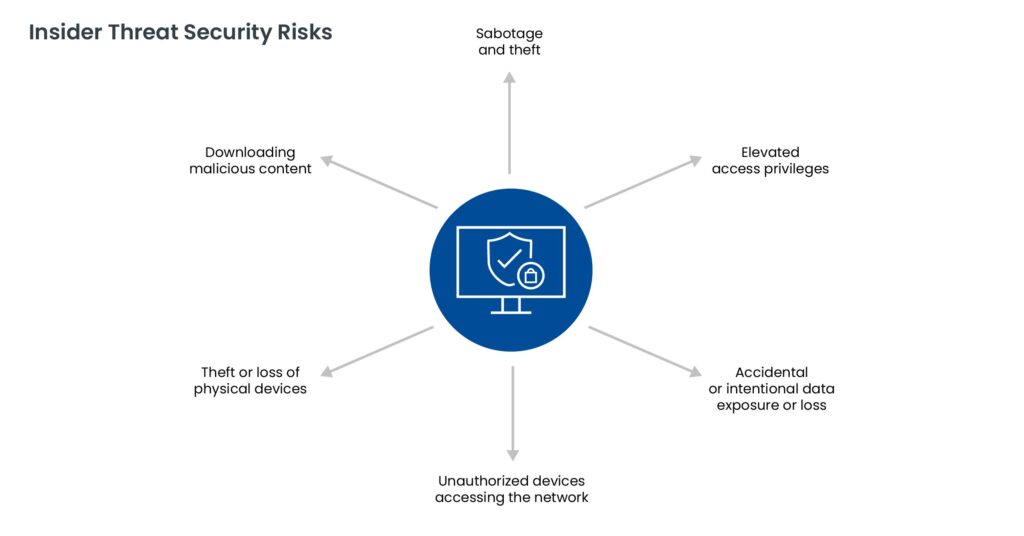
The typical lifecycle of an insider threat attack includes:
Insider threats can lead to severe consequences for organizations:
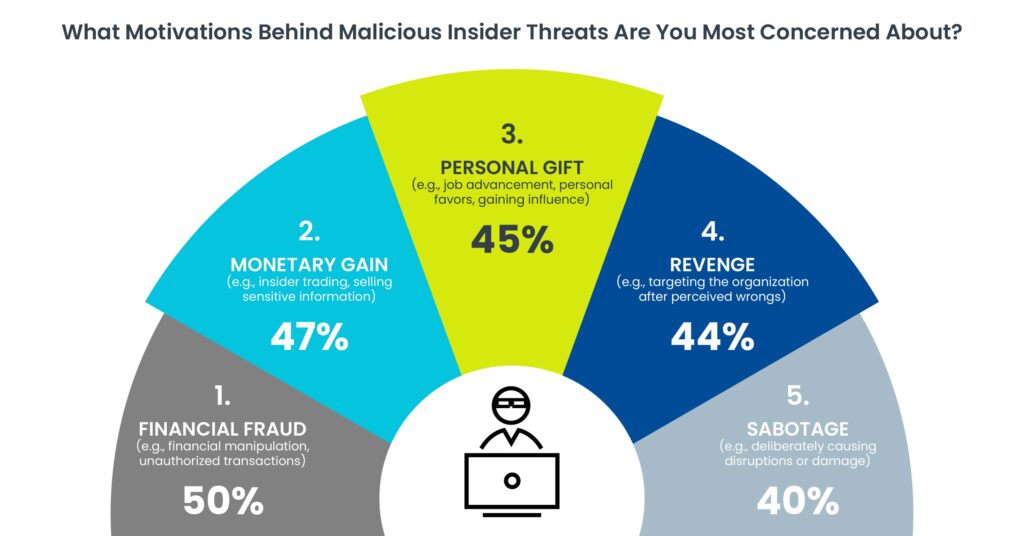
Organizations can take several measures to safeguard against insider threats:
Insider threats can often be more difficult to detect than external attacks since the perpetrators have legitimate access to internal systems. This makes it essential for organizations to balance trust with vigilance. By actively monitoring user activity, limiting access, and creating a culture of security awareness, businesses can reduce the risk of insider attacks.